|
|
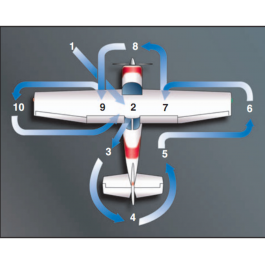
PreflightDescriptionFrom the Private Pilot ACS on what checklist should be used (the appropriate checklist) for the preflight. Click on the image below for a larger view. Here is the FAA's Safety Alert for Operators SAFO 17006 on why you need to use proper checklist Here are proper checklist for WIFA aircraft FAA's Advanced Preflight Pamphlet Click here for items to be sure and check during your preflight inspection Below is a link to a FAA Webinar. One of the topics discussed is cowl fasteners. You should not fly with cowl fasteners missing. In the video below, they also discuss how discrepancies should be handled. If you see oil or fluid under the brake caliper, be sure to check your brakes very carefully before departing. See pictures below on what to look for.  From the private pilot ACS: Knowledge - The applicant demonstrates understanding of: PA.II.A.K1 Pilot self-assessment. PA.II.A.K2 Determining that the airplane to be used is appropriate and airworthy. PA.II.A.K3 Airplane preflight inspection including: PA.II.A.K3a a. Which items must be inspected PA.II.A.K3b b. The reasons for checking each item PA.II.A.K3c c. How to detect possible defects PA.II.A.K3d d. The associated regulations PA.II.A.K4 Environmental factors including weather, terrain, route selection, and obstructions. Risk Management - The applicant demonstrates the ability to identify, assess and mitigate risks, encompassing: PA.II.A.R1 Pilot. PA.II.A.R2 Aircraft. PA.II.A.R3 Environment (e.g., weather, airports, airspace, terrain, obstacles). PA.II.A.R4 External pressures. PA.II.A.R5 Aviation security concerns. Skills - The applicant demonstrates the ability to: PA.II.A.S1 Inspect the airplane with reference to an appropriate checklist. PA.II.A.S2 Verify the airplane is in condition for safe flight and conforms to its type design. From the commercial pilot ACS: Knowledge - The applicant demonstrates understanding of: CA.II.A.K1 Pilot self-assessment. CA.II.A.K2 Determining that the airplane to be used is appropriate and airworthy. CA.II.A.K3 Airplane preflight inspection including: CA.II.A.K3a a. Which items must be inspected CA.II.A.K3b b. The reasons for checking each item CA.II.A.K3c c. How to detect possible defects CA.II.A.K3d d. The associated regulations CA.II.A.K4 Environmental factors including weather, terrain, route selection, and obstructions. Risk Management - The applicant demonstrates the ability to identify, assess and mitigate risks, encompassing: CA.II.A.R1 Pilot. CA.II.A.R2 Aircraft. CA.II.A.R3 Environment (e.g., weather, airports, airspace, terrain, obstacles). CA.II.A.R4 External pressures. CA.II.A.R5 Aviation security concerns. Skills - The applicant demonstrates the ability to: CA.II.A.S1 Inspect the airplane with reference to an appropriate checklist. CA.II.A.S2 Verify the airplane is in condition for safe flight and conforms to its type design. From the flight instructor PTS: Objective: To determine that the applicant: 1. Exhibits instructional knowledge of the elements of a preflight inspection, as applicable to the airplane used for the practical test, by describing: a. Reasons for the preflight inspection, items that should be inspected, and how defects are detected. b. Importance of using the appropriate checklist. c. How to determine fuel and oil quantity and contamination. d. Detection of fuel, oil, and hydraulic leaks. e. Inspection of the oxygen system, including supply and proper operation (if applicable). f. Inspection of the flight controls and water rudder (if applicable). g. Detection of visible structural damage. h. Removal of tie-downs, control locks, and wheel chocks. i. Removal of ice and frost. j. Importance of the proper loading and securing of baggage, cargo, and equipment. k. Use of sound judgment in determining whether the airplane is airworthy and in condition for safe flight. 2. Exhibits instructional knowledge of common errors related to a preflight inspection by describing: a. Failure to use or the improper use of checklist. b. Hazards which may result from allowing distractions to interrupt a visual inspection. c. Inability to recognize discrepancies to determine airworthiness. d. Failure to ensure servicing with the proper fuel and oil. e. Failure to ensure proper loading and securing of baggage, cargo, and equipment. 3. Demonstrates and simultaneously explains a preflight inspection from an instructional standpoint. Click here a FAA article regarding the preflight PvtLP, InstLP, ComLP, CFILP, CFIILP, MultiLP, MEILP, SeaplaneLP, MiscLP Detailed Information
|